Local Context Normalization: Revisiting Local Normalization
Normalization layers have been shown to improve convergence in deep neural networks, and even add useful inductive biases. In many vision applications the local spatial context of the features is important, but most common normalization schemes including Group Normalization (GN), Instance Normalization (IN), and Layer Normalization (LN) normalize over the entire spatial dimension of a feature. This can wash out important signals and degrade performance. For example, in applications that use satellite imagery, input images can be arbitrarily large; consequently, it is nonsensical to normalize over the entire area. Positional Normalization (PN), on the other hand, only normalizes over a single spatial position at a time. A natural compromise is to normalize features by local context, while also taking into account group level information. In this paper, we propose Local Context Normalization (LCN): a normalization layer where every feature is normalized based on a window around it and the filters in its group. We propose an algorithmic solution to make LCN efficient for arbitrary window sizes, even if every point in the image has a unique window. LCN outperforms its Batch Normalization (BN), GN, IN, and LN counterparts for object detection, semantic segmentation, and instance segmentation applications in several benchmark datasets, while keeping performance independent of the batch size and facilitating transfer learning.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2020 PDF CVPR 2020 Abstract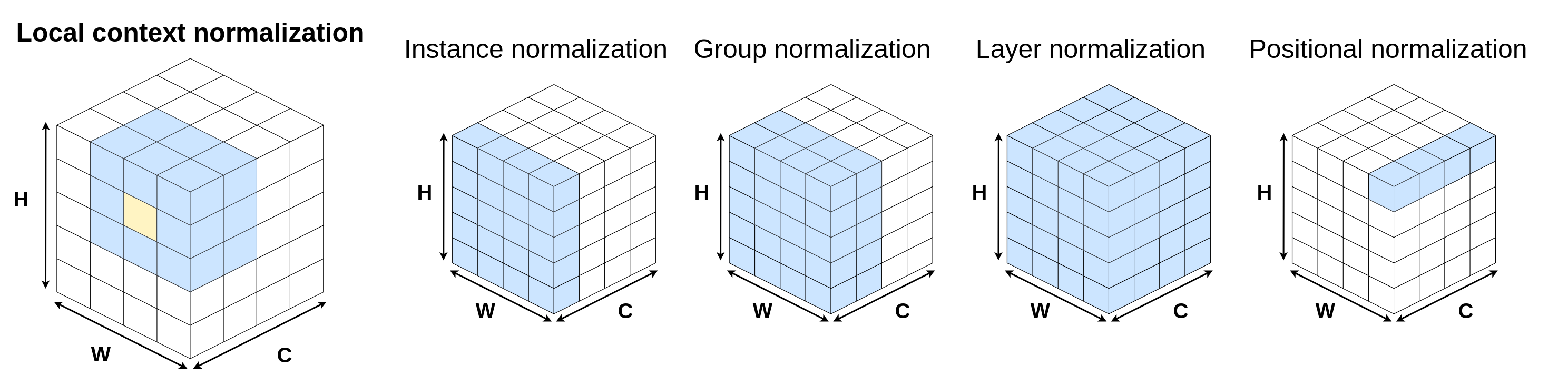






 ImageNet
ImageNet
 MS COCO
MS COCO