Robust active flow control over a range of Reynolds numbers using an artificial neural network trained through deep reinforcement learning
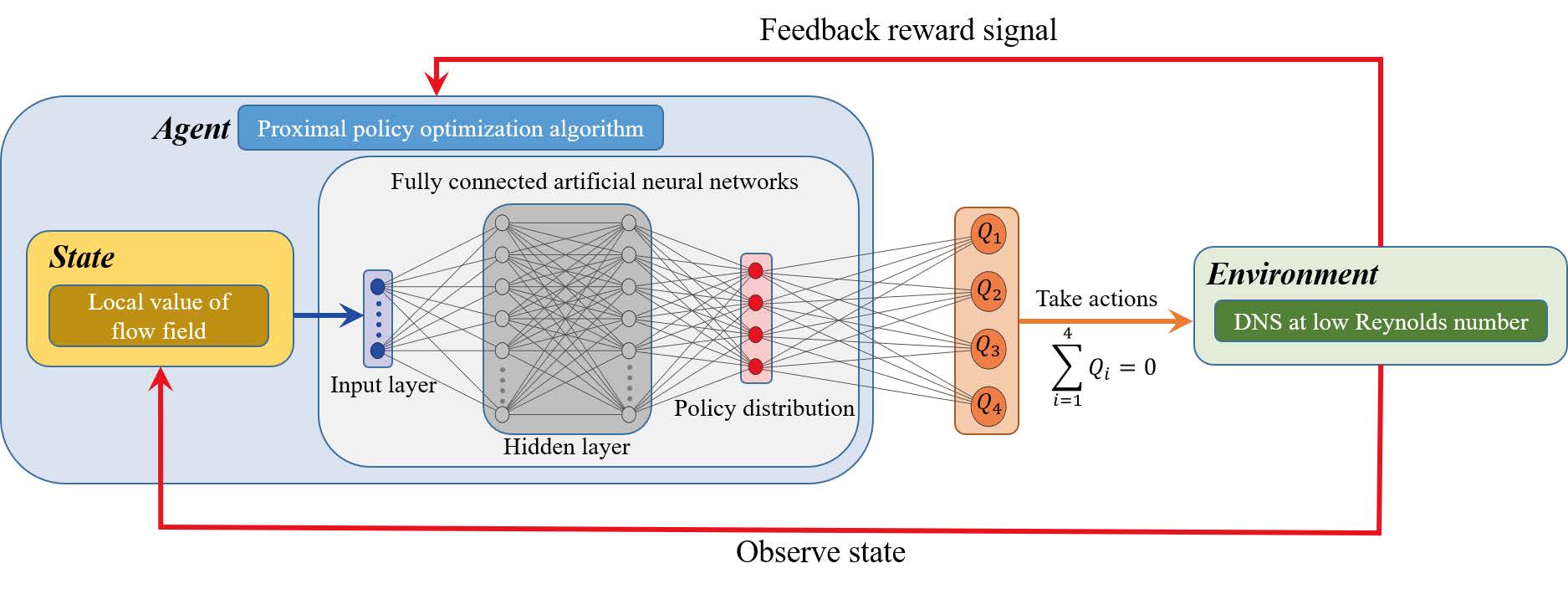
This paper focuses on the active flow control of a computational fluid dynamics simulation over a range of Reynolds numbers using deep reinforcement learning (DRL). More precisely, the proximal policy optimization (PPO) method is used to control the mass flow rate of four synthetic jets symmetrically located on the upper and lower sides of a cylinder immersed in a two-dimensional flow domain. The learning environment supports four flow configurations with Reynolds numbers 100, 200, 300 and 400, respectively. A new smoothing interpolation function is proposed to help the PPO algorithm to learn to set continuous actions, which is of great importance to effectively suppress problematic jumps in lift and allow a better convergence for the training process. It is shown that the DRL controller is able to significantly reduce the lift and drag fluctuations and to actively reduce the drag by approximately 5.7%, 21.6%, 32.7%, and 38.7%, at $Re$=100, 200, 300, and 400 respectively. More importantly, it can also effectively reduce drag for any previously unseen value of the Reynolds number between 60 and 400. This highlights the generalization ability of deep neural networks and is an important milestone to active flow control.
PDF Abstract