Finite resonance widths influence thermal model description of hadron yields
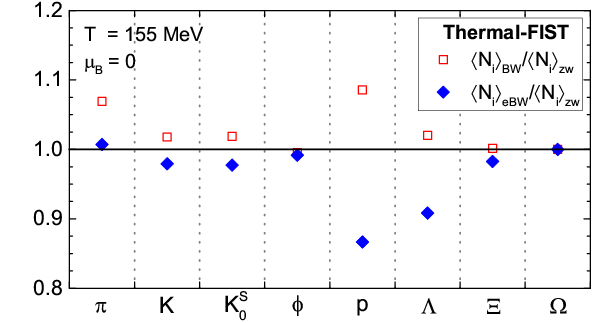
Different scenarios for modeling resonances in a thermal model description of hadron yields measured in heavy-ion collisions are explored: the zero-width approximation, the energy independent Breit-Wigner scheme, and the energy dependent Breit-Wigner (eBW) scheme. Application of the eBW scheme leads to a notable suppression in the proton yields, stemming mainly from a reduced feeddown from $\Delta$ resonances because of the threshold effects. A significantly improved agreement of thermal model with hadron yields measured in Pb-Pb collisions at $\sqrt{s_{_{NN}}} = 2.76$ TeV by the ALICE collaboration is obtained in the eBW scheme at $T \simeq 155$ MeV, indicating a possible resolution of the so-called 'proton puzzle'. The results obtained show that there are significant systematic uncertainties in the thermal model due to the modeling of broad resonances.
PDF Abstract