Improving CTC-based speech recognition via knowledge transferring from pre-trained language models
Recently, end-to-end automatic speech recognition models based on connectionist temporal classification (CTC) have achieved impressive results, especially when fine-tuned from wav2vec2.0 models. Due to the conditional independence assumption, CTC-based models are always weaker than attention-based encoder-decoder models and require the assistance of external language models (LMs). To solve this issue, we propose two knowledge transferring methods that leverage pre-trained LMs, such as BERT and GPT2, to improve CTC-based models. The first method is based on representation learning, in which the CTC-based models use the representation produced by BERT as an auxiliary learning target. The second method is based on joint classification learning, which combines GPT2 for text modeling with a hybrid CTC/attention architecture. Experiment on AISHELL-1 corpus yields a character error rate (CER) of 4.2% on the test set. When compared to the vanilla CTC-based models fine-tuned from the wav2vec2.0 models, our knowledge transferring method reduces CER by 16.1% relatively without external LMs.
PDF Abstract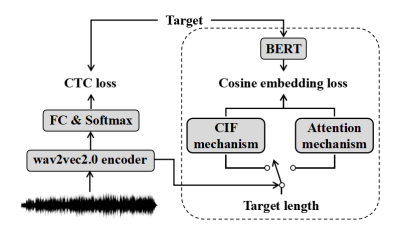





 AISHELL-1
AISHELL-1