DeepLesionBrain: Towards a broader deep-learning generalization for multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation
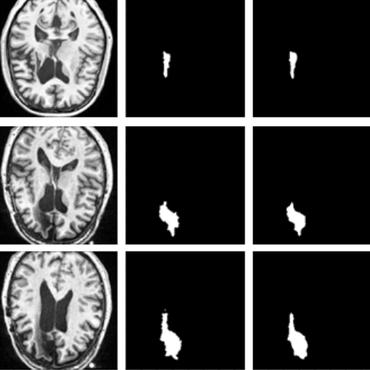
Recently, segmentation methods based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) showed promising performance in automatic Multiple Sclerosis (MS) lesions segmentation. These techniques have even outperformed human experts in controlled evaluation conditions such as Longitudinal MS Lesion Segmentation Challenge (ISBI Challenge). However state-of-the-art approaches trained to perform well on highly-controlled datasets fail to generalize on clinical data from unseen datasets. Instead of proposing another improvement of the segmentation accuracy, we propose a novel method robust to domain shift and performing well on unseen datasets, called DeepLesionBrain (DLB). This generalization property results from three main contributions. First, DLB is based on a large group of compact 3D CNNs. This spatially distributed strategy ensures a robust prediction despite the risk of generalization failure of some individual networks. Second, DLB includes a new image quality data augmentation to reduce dependency to training data specificity (e.g., acquisition protocol). Finally, to learn a more generalizable representation of MS lesions, we propose a hierarchical specialization learning (HSL). HSL is performed by pre-training a generic network over the whole brain, before using its weights as initialization to locally specialized networks. By this end, DLB learns both generic features extracted at global image level and specific features extracted at local image level. DLB generalization was validated in cross-dataset experiments on MSSEG'16, ISBI challenge, and in-house datasets. During experiments, DLB showed higher segmentation accuracy, better segmentation consistency and greater generalization performance compared to state-of-the-art methods. Therefore, DLB offers a robust framework well-suited for clinical practice.
PDF Abstract